12
www.techno-isel.com
Technical Information
Raceways
Filling slots
Rolling Element Bearings, or roller bearings, make up the bulk of
commercially available and applied bearings. These types of bearings
rely on either balls or rollers to carry the load. The rolling motion
produces less friction than found in plain bearings. For this reason,
roller bearings are also referred to as antifriction bearings. Both radial
loads and thrust loads can be supported by this type of bearing.
Lubrication is either permanently sealed in the bearing or is required
during operation. The largest causes of failure are either exceeding
temperature, load and speed limits, or providing insufficient lubrication
during operation. Since roller bearing applications often involve heavy
loads and high speeds, failure can be catastrophic, extremely costly
and time consuming to repair. Usually there will be an increase in the
sound of the balls or rollers in the raceways when approaching failure.
There are many different configurations of roller element bearings, and
some are discussed in the following section.
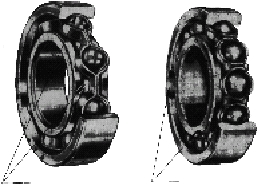
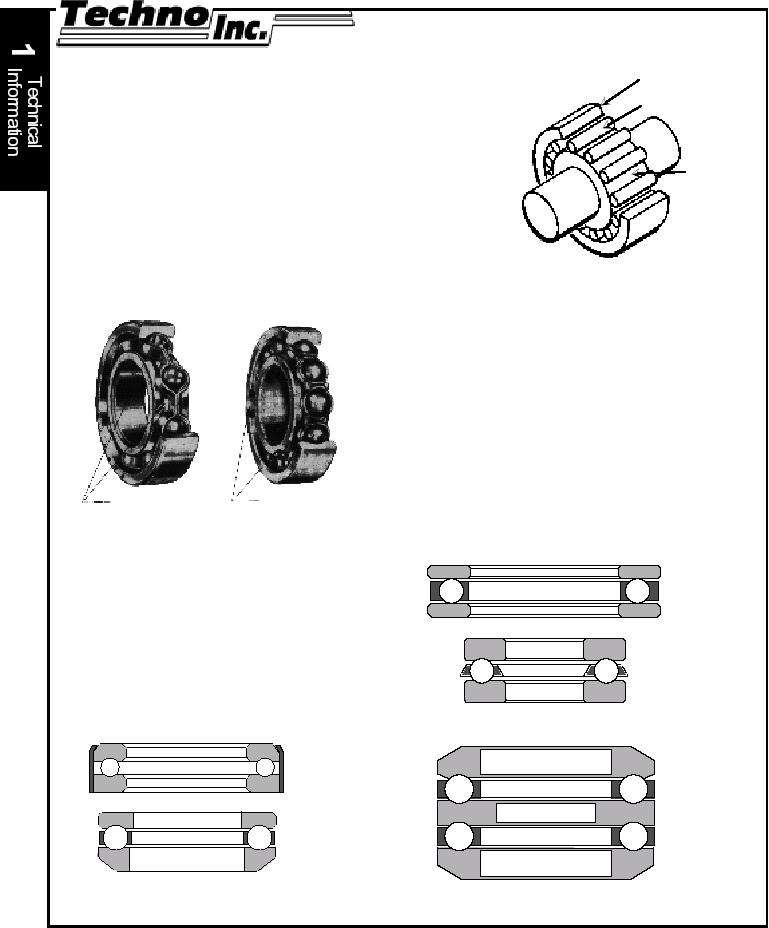
Radial Ball Bearings come in two basic variations which
are called the Conrad type, or nonfilling slot, and the
maximum capacity type, or filling slot. The Conrad type has
a deep, uninterrupted raceway in inner and outer rings. This
design is capable of carrying heavy radial and moderate bi-
directional thrust loads. The maximum capacity bearing has
more balls than an equivalent sized Conrad type, therefore
carries a higher radial load. However, the filling slots require
that the thrust loads be light and applied only in combination
with a heavier radial load. If moderate thrust loads are
present, the maximum type can be replaced by a double
row Conrad type bearing. Selection of this type bearing is
outlined in the following section.
Thrust Ball Bearings are designed to
provide axial shaft location and support
thrust loads. Angular contact ball
bearings support radial as well as thrust
loads, and the ratio of permissible radial
to thrust loads depends upon the angle
of contact between the races and the
bearing axis. Thrust ball bearings are
commonly used in linear motion
systems to support the drive screw.
Conrad-type ball bearing, left, and
maximum-capacity (filling slot) type, right
Flat-race, flat-seat thrust ball bearing, A, and
grooved-race, flat-seat thrust ball bearing, B
Aligning, double-acting, grooved-race
thrust ball bearing
A
B
Banded thrust ball bearing, A, and
aligning, single-acting, grooved-race
thrust ball bearing, B
B
A
Outer race
Rolling element
Inner
Race
ROLLING ELEMENT